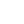Have you ever wondered where the term “March Madness” comes from? You may think it was a term coined by news broadcasters or advertisers to describe the excitement of the NCAA basketball final showdown. However, the popular phrase is credited to an Illinois high school official, Henry V. Porter, who in 1939 used the term to describe the Illinois High School Basketball Annual Championships. At one time, more than 900 teams would battle it out for the state title at the University of Illinois’ Huff Gymnasium. The term was later made even more illustrious by CBS broadcaster Brent Musburger, who used the term in the 1982 men’s NCAA basketball tournament.
While March Madness usually evokes images of incredible upsets, broken brackets, and history-making moments, it can also describe the current madness unfolding regarding the future direction of the U.S. economy. The first 100 days of a president’s term are typically marked by cabinet confirmations, settling into the White House, collaborating with Congress on legislation, and issuing executive orders. President Donald Trump seems particularly fond of the last item on that list, potentially busting social and economic bracket predictions across the nation. During his first term, Trump signed 24 executive orders in his first 100 days. This time around, he’s signed 96, with more likely before the April 30, 2025, milestone. By comparison, Joe Biden issued 162 executive orders during his term as President of the United States.
The dreaded T in basketball often connotes angry outbursts and a point-scoring opportunity for opponents. In economic circles, the feared T stands for tariffs, which also creates potential winners and losers within global competitive trade. President Trump has already issued several executive orders surrounding tariffs and is keeping his thumb on the buzzer to increase or decrease tariff levels depending on how market participants react to his defensive and offensive maneuvers. The situation looks quite volatile for the viewers in the grandstands with new matchups and strategies occurring daily. With the Administration coveting the team from Greenland one day while taunting the Canadian team as the 51st draft pick the next. So far, Trump’s toughest matchups have been with its biggest trading partners – China, Canada, Mexico, Colombia, and the European Union, with each country playing its own defense or sometimes giving in to the full-court pressure. Here is a recap of some of the important tariff definitions and matchups, and what sectors are the key players.
Tariffs are taxes levied by governments on imported or exported goods. The main types of tariffs include: Ad Valorem — calculated as a percentage of the good’s value (e.g., 10% of a car’s price), Specific — a fixed amount per unit (e.g., $5 per ton of steel), and Compound — a combination of both. Tariffs serve various purposes, such as protecting domestic industries from foreign competition, generating government revenue, and responding to unfair trade practices by other countries. Before 1913, the U.S. government relied entirely on tariffs for funding. However, the introduction of the income tax in 1913 fundamentally altered the nation’s revenue structure.
At a high level, pro-tariff arguments suggest that tariffs protect U.S. jobs and promote local businesses by shielding them from international competition. On the other hand, anti-tariff perspectives contend that tariffs drive up costs, reduce market efficiency, and negatively impact global trade.
Match up #1: United States vs. China
It’s no surprise that President Trump’s top rival is the world’s second-largest economy — China. Chinese President Xi Jinping and President Donald Trump have had their share of one-on-one matchups in the past. During Trump’s first term, the United States entered a trade war with its largest trading partner at the time, resulting in a significant decline in Chinese imports since 2018 — a trend that’s likely to continue.
Source: Wall Street Journal
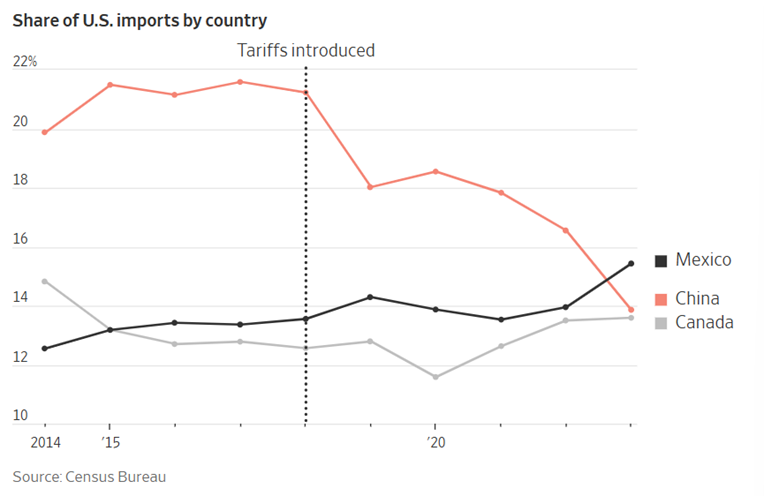
President Biden left many of the tariffs in place from Trump’s first term. Trump’s America First plan includes raising tariffs by another 10%. In retaliation, China has declared it will impose an additional 15% tariff on U.S. chicken, wheat, corn, and cotton products, while American sorghum, soybeans, pork, beef, seafood, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products will face an extra 10% tariff. U.S. Agricultural experts are concerned about the additional tariffs as the U.S. farm economy is coming off lower net farm incomes in 2024 and falling commodity prices. China was the largest importer of U.S. agricultural goods in 2023; however, the previous China tariff regime resulted in the emergence of Brazil as a supplier of bulk commodities to China in recent years. U.S. farmers will likely be in the center lane if additional tariffs are levied on China over the next few years.
Source: USDA
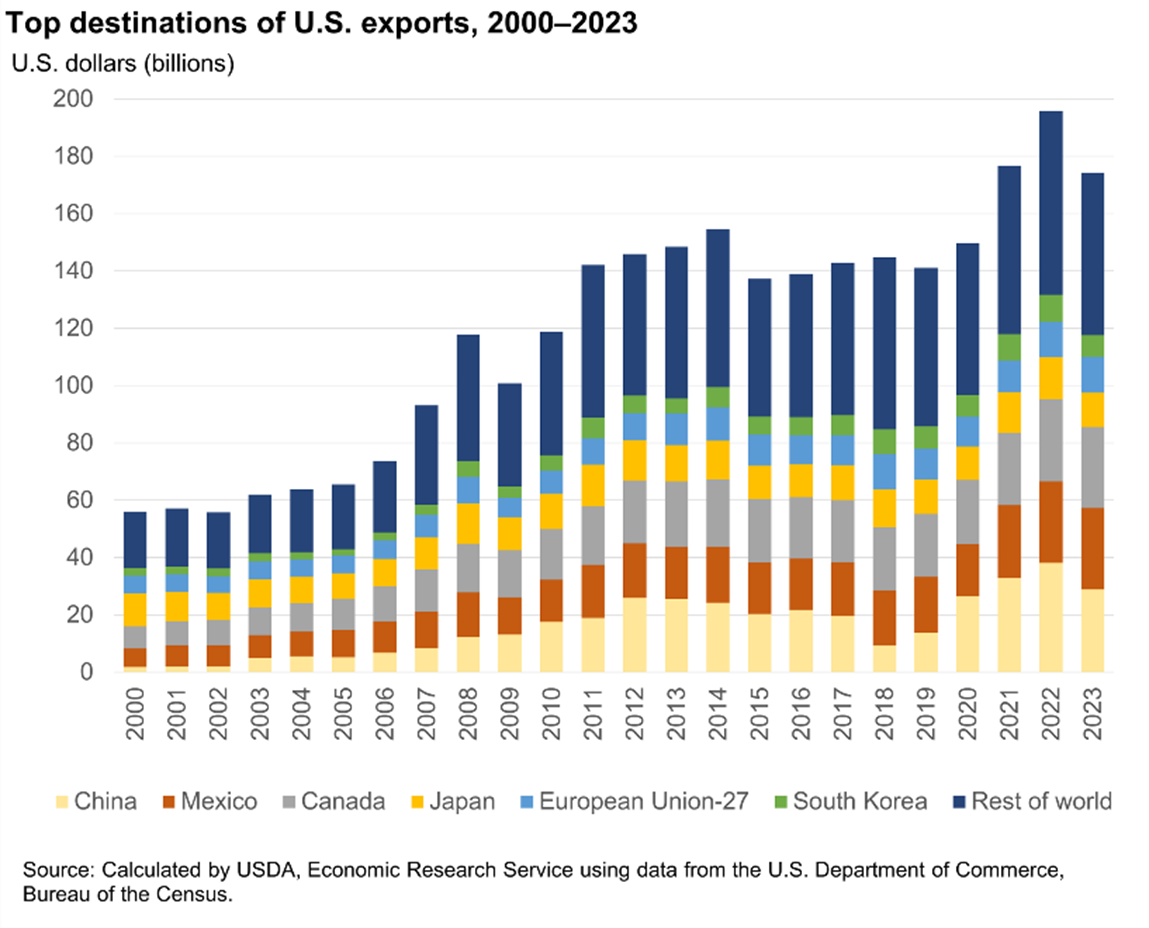
On the import side of the equation, several items will likely see price increases in the next few years. You can find the “Made in China” label on everything from your clothing tags to car parts, cell phones, and other tech devices. As one of the dominant producers in the semiconductor industry, China has been running a fast break in the United States on smartphones, computers, and electronic appliances for years. President Trump has vowed to increase domestic chip production during his presidency, a promise that former President Biden also made. While Biden attempted to boost domestic production through subsidies and tax incentives, Trump is taking a more aggressive approach using his entire bench of economic levers. Trump has discussed scrapping the Inflation Reduction Act infrastructure legislation and insisted that higher tariffs would incentivize manufacturers to move production to the United States. It’s still early days, but some global technology stalwarts have read “the art of the deal” playbook and are making commitments to onshore critical technology manufacturing and services to the U.S. The boxscore highlights include $1.3 trillion from a) Apple for $500 billion, b) AI infrastructure led by OpenAI, Oracle, and SoftBank of $500 billion, c) Taiwan Semiconductor (TSMC) of $100 billion, and d) Nvidia of $200 billion.
Source: Wall Street Journal
Match up #2: United States vs. Canada
Much like the battles associated with the recent Four Nations Face-Off hockey tournament, the U.S. and Canada are once again clashing amid the ongoing tariff madness — let’s just hope no one loses their teeth this time. Relations with our northern neighbor have been tense, especially after President Trump’s provocative remarks about Canada becoming the U.S.’s 51st state. While that scenario is a bit far-fetched, one thing that’s more certain is that our pancake breakfasts might get pricier from the rising cost of Canadian maple syrup.
Frustrated by immigration issues and the fentanyl crisis, Trump imposed a 25% tariff on goods coming in from both Canada and Mexico, despite Canada contributing only a small fraction of the fentanyl entering the U.S. In response, Canada slapped a 25% duty on select goods, notably steel and aluminum. This back-and-forth is hitting some American car manufacturers hard, even as they’re already grappling with rising costs due to increased tariffs on Chinese semiconductors. Early estimates suggest that the price of a new car could rise by as much as $4,000 to $10,000 — the economic equivalent of watching your #1 seed get knocked out by a #16.
Spectators: The American Consumer
Waiting anxiously in the stands is the American consumer, unsure of how these tariffs will play out. On one hand, tariffs mean increased revenue for the U.S. government — a much-needed boost as it grapples with a growing deficit. President Trump campaigned on promises to reduce the budget deficit and has already cut thousands of federal jobs to rein in government spending. However, the legality of some of these executive branch actions remains subject to judicial challenges.
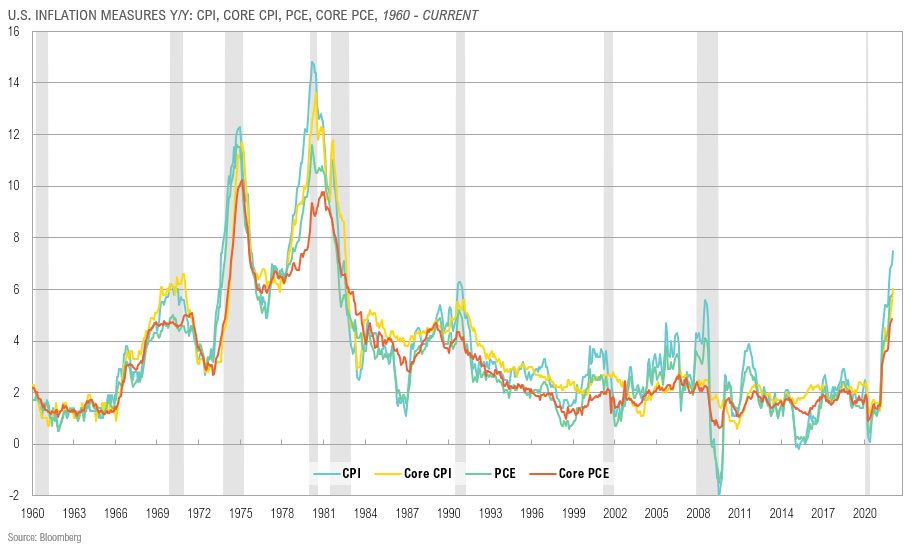
Historically, increased tariffs are typically passed on to the consumer through price increases, and it is rare for companies to absorb the increased costs entirely. With the volatility of the situation, it is unclear how much, if any, of the tariff burden will be passed along to U.S. consumers, but some consumers are already starting to hold tighter to their playbook. Consumer sentiment took a hard foul in March, with the University of Michigan’s survey showing a 10.5% drop from February, hitting its lowest point since November 2022. Inflation concerns and market volatility played tough defense. The one-year inflation outlook soared to 4.9%, its highest since November 2022, while long-term expectations posted numbers not seen since 1993 — a throwback no one was cheering for. Sentiment fell across political lines, with overall expectations taking a 22% slide since December. It will be interesting to see how future consumer sentiment reports reflect the evolving landscape surrounding tariffs. Despite the rough court conditions, markets have generally held their ground, eyeing the Federal Reserve for potential rate cuts later in the game.
Spectators: Financial Markets
The current tariff strategy has financial markets waiting for the brackets to bust. Initially, stocks showed confidence and optimism, rising 2.5% after the election outcome was announced. However, equity markets have reversed all those gains in recent weeks, with the S&P 500 declining 3.6% since November 5th. The Trump Administration has not ruled out the possibility of a recession as they try to rebalance the budget and the fiscal picture for long-term sustainability by eliminating waste, fraud, and abuse in government spending and boosting revenues sourced from foreigners through tariffs and other means. Investors are looking to real assets like gold as their 6th man, hoping for a solid defense against global volatility from a rebalancing of trade and monetary regimes.
The Final Countdown
As the final buzzer looms on President Trump’s first 100 days back in office, the tariff madness shows no signs of letting up. Each new policy feels like a buzzer-beater, shifting momentum and keeping markets, consumers, and global trade partners on their toes and in a defensive posture. Much like a championship game, every move sparks reactions — from retaliatory tariffs to shifting supply chains and rising costs. Farmers brace for a tougher growing season ahead, manufacturers scramble to adjust sourcing plans, and consumers anxiously await the final score on prices at checkout.
Financial markets remain in a full-court press, with investors hedging bets with flight to safety plays like gold, hoping to avoid getting benched by volatility. Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve stands on the sidelines, watching for signs that the economy needs a timeout — or perhaps a rate cut — to ease mounting economic worries.
Whether these Trump tariff policies lead to long-term gains or a costly turnover is still up for debate. One thing is certain: the tariff madness isn’t over, and the next few quarters promise more surprises, more drama, and plenty of action before the final whistle blows. For now, all we can do is watch the game unfold — brackets busted and all.
Readers looking to sit in on the Team Trump’s sideline huddle on tariffs and economic strategies can watch the All-In Podcast’s Interview of Commerce Secretary Lutnick at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=182ckTL2KBA.