On the field that is the U.S. economy, currently loading the bases are looming interest rate hikes, the value of the U.S. dollar, and rising Treasury yields. On the mound, is Federal Reserve Chairman, Jerome Powell, and everyone from investors to consumers are waiting to see what will happen next with monetary policy and the economy. Early in the game, the COVID-19 pandemic threw a curveball, and ever since, the economy has been dribbling a series of weak grounders from persistent unemployment, to supply chain disruptions and a declining labor force participation rate. Will Chairman Powell toe the rubber to strike out runaway inflation and imperil economic growth or is the US economy in for extra innings?
How did inflation get so out of hand?
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that in January 2022, the consumer price index rose 7.5% from January 2021, the highest rate of inflation since February of 1982. Some of the industries seeing the largest price hikes are the energy, gasoline, housing, and food sectors which is of no surprise for anyone who has bought groceries or visited the gas pump lately. Even with the rise in prices, it hasn’t generally stopped consumers from spending. The Commerce Department reported that retail sales are up 3.8% year over year with large gains reported in vehicle, furniture, and building supply purchases. Home sales have been on the rise as well with the National Association of Realtors citing that home sales in January were up 6.7% from the previous month. This comes as home buyers are trying to secure financing at lower interest rates before the anticipated Federal Reserve rate increase next month.
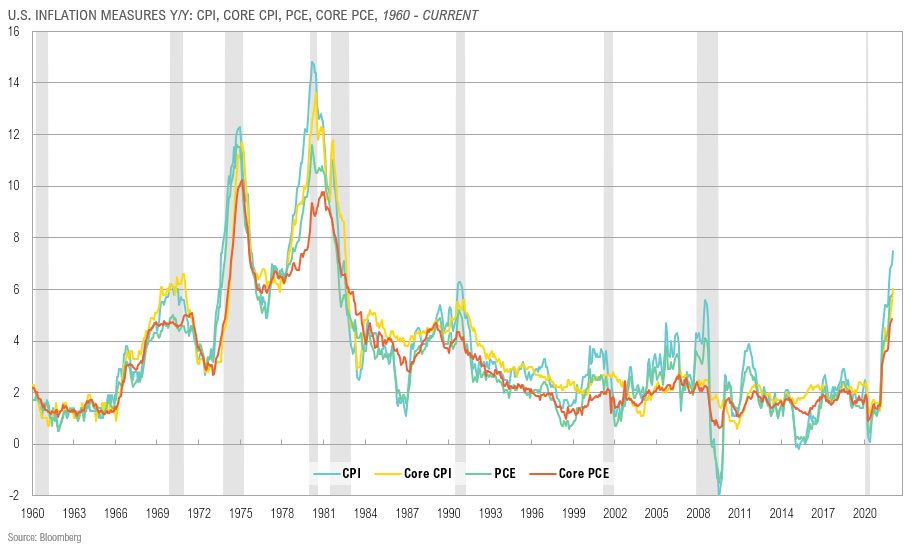
Source: SpringTide US. Inflation Trends
While this level of inflation is unlike anything Americans born after the 1970s and early ‘80s have ever experienced, many economists are not surprised by this spike in the CPI. The federal government has shelled out more than $3.5 trillion in COVID-19 relief funding in the form of stimulus checks, unemployment compensation, and the paycheck protection program. The figure below shows the allocation of this spending with more spending earmarked through 2030 as the government continues to combat the aftershocks of the pandemic. The excess liquidity in the market, combined with the supply chain disruptions and labor shortages, has created the perfect cocktail for inflation to brew. While this spending was necessary to keep the economy out of a recession, some argue the federal reserve hasn’t been aggressive enough in unwinding its pandemic era policies to combat rising inflation. The Federal Reserve has announced that rates will start to rise in March, but by how much? Experts, such as economists at Citibank, are predicting anywhere from a 25 to 50-basis point hike with the later end of the spectrum becoming more likely as inflation rises. They are then expecting three to four more 25-basis point hikes by the end of 2022. Economists feel this could help slow inflation by the end of the year, but supply chain disruptions and incipient wage inflation risk still loom.

Source: CNBC analysis of Treasury data compiled by the Pandemic Response Accountability Committee
Is 2022, the new 1980?
The survivors of the last battle with inflation in the 1970s and 80s know all too well what runaway inflation looks like. It has some questioning whether we are in for a blast from the past in 2022. Inflation peaked in 1980 at 14.8% and while we haven’t hit those levels yet, the jump we have experienced has people on their toes for a line drive heading for them. Inflation in the ’80s was driven by a variety of factors from unpredictability in interest rates to soaring oil prices. Most economists believe that this time is different than the 1980s as recent inflation has been caused by COVID-19 aftershocks of excess liquidity and supply chain issues. These factors are expected to normalize over time.
Examining our Investment Strategy
Markets have been off to a shaky start in 2022 with inflation and geopolitical risks in Russia & Ukraine driving the recent volatility. Economists and investors worry that if war broke out between Ukraine and Russia, it could cause more supply chain disruptions of commodities which could prolong inflation. While the Federal Reserve’s announcement of a March interest rate increase has curbed some concerns about more inflation, these new geopolitical risks could overshadow efforts to reduce inflation through monetary policy. As a result, investors are watching markets closely in addition to exploring inflation-protected physical assets such as gold or farmland. Below is the historical correlation between several asset classes and the consumer price index using returns data from 1970-2020. The CPI has historically had a positive relationship with bonds and precious metals but a negative relationship with equities.
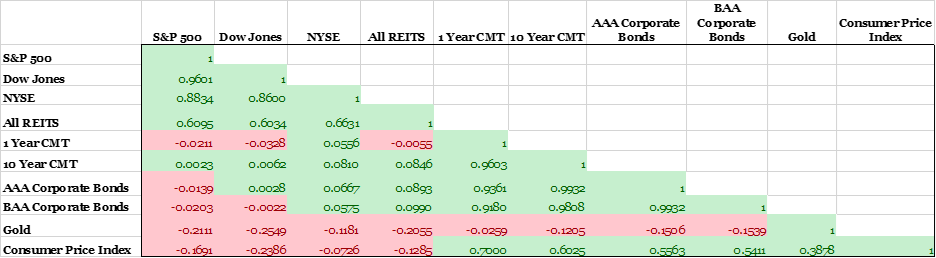
Source: Data supplied by the TIAA Center for Farmland Research
Physical assets such as precious metals and farmland have taken center stage the past few months with gold values up 5.3% year to date and farmland values up 22% in parts of the Midwest since this time last year. While these physical assets have been investors’ go-to during high inflationary periods in the past, investors have also been allocating more of their portfolios to cryptocurrencies as well. Cryptocurrencies have a relatively short history compared to traditional assets which makes it difficult to analyze their performance with inflation, however, some investors are calling it “digital gold.” Even Mr. Wonderful, Kevin O’Leary, claims that his portfolio has more holdings in cryptocurrencies now than gold. Crypto enthusiasts cite its ability to be shielded from the effects of government money printing and spending largesse.
Servant Financial has been keeping tabs on inflation and has updated its investing strategy accordingly based on investors’ risk tolerance. While we are still allocating a portion of portfolios to equities and fixed income instruments, we’ve had a higher portfolio tilt towards allocation to precious metals, real assets, and Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (BTC) as protection for client portfolios from inflation. INFL, Horizon Kinetics Inflation Beneficiaries ETF, has recently been added to the portfolio as well. It is an actively managed ETF designed to capitalize on growing inflation trends. Currently, INFL has $896 million assets under management with holdings in transportation, financial exchanges, energy and food infrastructure, real estate, and mining companies. While INFL has a diverse group of global holdings, its top holdings are in PrairieSky Royalty (Oil & Gas), Archer Daniels Midland (Food & Agribusiness Processing), and Viper Energy Partners (Oil & Minerals).
While inflation has threatened investors’ portfolio returns, an adjustment in investment strategy for the purposes of inflation hedging will help investors score in the performance game in the later innings of this economic cycle. A watchful eye must be kept on key economic signals such as changes in interest rates, inflation trends globally, and the supply chain normalization. If you would like to discuss your asset allocation so you can do well in all facets of the investment game like the alert and observant Willie Mays, the Say Hey Kid (Say who. Say what. Say where. Say hey.), contact Servant Financial today.