The digital economy is an umbrella term that describes how traditional brick-and-mortar activities are being disrupted or altered by the Internet and blockchain technologies. The institutionalization of digital assets throughout history has been driven by various factors, including shifts in investor risk preferences or changes in economic conditions, but most importantly by advancements and convergences in technology and related network effects. Network effects are a phenomenon whereby a product or service gains additional economic value as more people use it. Think of social media networks Facebook and Twitter, e-commerce platforms like Amazon or Apple’s app store and iPhone, or digital payment platforms like PayPal, Venmo, or Bitcoin.
The institutionalization of “tangible” digital assets began with the proliferation of digital real estate assets over the last few decades. The emergence of these new real assets has been driven by a massive secular movement from analog to digital systems and the development of real assets and infrastructure to support the digitization of economic activities and an ever-increasing array of new digital technologies. Below are a couple of examples of ubiquitous digital real estate assets that have emerged over recent decades:
Cell Towers: Cell towers are perhaps one of the earliest examples of new digital real assets that have undergone the institutionalization process. As mobile communication technology has developed to meet business and consumer demands for greater bandwidth and rich features, a massive infrastructure buildout has occurred to support network reliability and responsiveness. Cell towers provide the infrastructure necessary for wireless communication networks, and they generate revenue through leasing agreements with telecommunication service providers.
Institutional investors recognized the combination of stable income and the growth potential of cell towers and began investing in the asset class. Tower companies, REITs, and infrastructure funds were formed to acquire and manage portfolios of cell towers. We witnessed the successful development of this nascent asset class in the mid-2000s through a family office advisory relationship for which we oversaw a private equity fund exit of a private cell tower business to Crown Castle International (NYSE: CCI) for $5.8 billion and very rich multiples on invested capital and tower cash flows. These entities focus on leasing tower space to telecommunication companies, effectively creating a stream of relatively stable and growing rental income. Co-location of cellular equipment from multiple carriers on a single tower created interesting upside optionality and ultimately outsized returns for early cell-tower owners and investors.
Data Centers: With the rapid growth of the digital economy, data centers have emerged as a critical infrastructure asset necessary to support the increased digitization of communication and storage and retrieval of exponentially larger data elements. Data centers provide the physical infrastructure to store and process large amounts of digital information. Institutional investors recognized the increasing demand for data storage and processing capabilities, leading to the development of specialized data center investment firms and funds. Like cell towers, specialized public corporations and REITs were formed to hold these data center assets, such as Equinix, Inc. (Nasdaq: EQIX) and Digital Realty Trust, Inc. (NYSE: DLR)
Concurrently, Amazon was developing its own data center expertise and infrastructure in support of its online book-selling business and expansion into other consumer products. Ultimately, Amazon was able to monetize its cloud-computing and data center expertise by building out a hugely profitable outsourced data center management business within Amazon.com (NYSE: AMZN) called Amazon Web Service, or AWS for short. This unique company’s specific transformation illustrates the powerful confluence of learning curves, technological reinforcement, economies of scale, and/or network convergence that can be associated with the digitization of the economy.
The institutionalization of these two asset classes involved the entry of large-scale institutional investors, such as pension funds, insurance companies, venture capital, and private equity firms, who brought significant capital and professional management expertise. They often acquired substantial portfolios of assets within the specific asset class, creating economies of scale and professionalizing operations.
The institutionalization process typically involves the standardization of investment structures, the development of specialized investment vehicles (for example, the more tax-efficient REIT structure for holding qualifying real estate assets), and the establishment of industry best practices. Very often adjustments in the existing regulatory framework and industry practices are necessary to bridge compliance gaps. The institutionalization process generally contributes to increased liquidity, transparency, and stability within an asset class, ultimately making it more attractive to a wider range of investors. The REITs cited earlier are examples of these institutional market forces. I think one important lesson from this history is that you want to be an early investor in these emerging digital asset classes prior to the formation of public REIT structures that democratized the asset to the masses.
Importantly, smaller, and more nimble retail investors have a distinct advantage over institutional investors if they can identify the approaching institutionalization of an asset class in advance of the institutional capital pools and have the fortitude to invest in an emerging digital asset in the early adopter phase of the S-curve adoption patterns commonly taught in university business classes. The early adopter phase is typically after proof of concept but prior to mass market adoption and the large institutional capital flows.
As we’ve all experienced firsthand with the emergence of mobile communication enabled by cell towers and cloud computing enabled by data centers, the adoption rate of digital innovations tends to be non-linear. Adoption is generally slow at first driven by a small group of innovators. Adoption rates then torise rapidly as early adopters and then the early and later majority come on board in the mass market phase before adoption flattens out in the maturation phase. These traditional S-curve innovation adoption rate concepts are graphically depicted below:
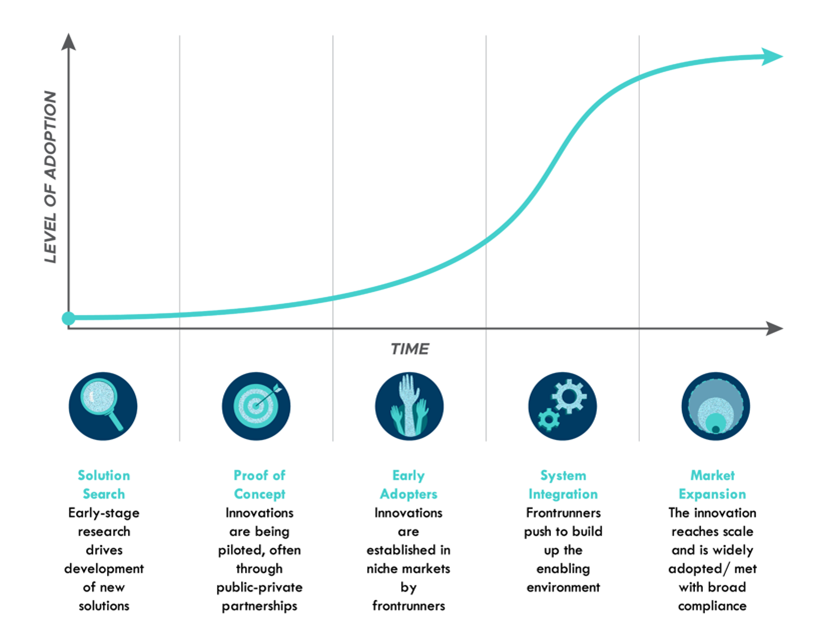
Levels of Adoption: Solution Search/Innovators: <2.5%, Proof of Concept/Early Adopters: 2.5% to 13.5%, System Integration/Early Majority: 13.5% to 50.0%, Market Expansion/Late Majority: 50.0% to 84%, and Laggards – last 16%
Source: Rocky Mountain Institute, “Harnessing the Power of S-Curves”
Bitcoinalization
According to a June 2022 analysis of Bitcoin User Adoption by Blockware Solutions, somewhere between 1% to 3% of the global population are bitcoin users/holders. This is a broad approximation because one on-chain entity could be a single person that self-custodies their bitcoin or it could be an exchange, custodian desk, or other institution that represents thousands or potentially millions of individuals.
Blockware Solutions’ analysis puts Bitcoin somewhere in the Early Adopters phase in the S-curve paradigm. System Integration is the next phase in the cycle and with it comes mass-market adoption. From this standpoint, bitcoin is at a critically important inflection point in its history. We’ve “coined” this coming wave of institutional adoption as bitcoinalization.
Before going into our investment case further, let’s look at the institutionalization process of a purely digital networked business more like bitcoin and distributed ledger technology (DLT) to supplement the foregoing tangible cell tower and data center examples. Some important patterns and potential impediments for future Bitcoin user adoption may become apparent.
One technology-enabled asset class institutionalization process that can be seen as an analogy for Bitcoin and DLT is the emergence of the Internet and the subsequent development of the digital advertising industry. As can be seen from the digital real estate examples, the Internet revolutionized the way information is shared, communicated, and accessed. The World-Wide Web provided a platform for new business models and created opportunities for new and innovative asset classes. One of these asset classes is digital advertising, which grew alongside the expansion of the Internet and digital real estate assets and infrastructure.
Correspondingly, bitcoin and DLT would not be possible without the Internet and associated global communication and data processing networks. Bitcoin and DLT have transformed the financial landscape by introducing decentralized digital currencies and distributed ledger systems. Bitcoin, as the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, paved the way for the institutionalization of digital assets and the exploration of blockchain-based technologies or distributed ledgers.
Similarities between the institutionalization processes of digital advertising and Bitcoin/DLT include:
Disintermediation: Both digital advertising and Bitcoin/DLT aim to eliminate intermediaries, reducing the need for trusted third parties. In digital advertising, the traditional intermediaries, advertising agencies, were bypassed as digital platforms enabled direct connections between advertisers and consumers. Similarly, Bitcoin and DLT aim to create a trustless system where transactions can occur directly between participants without financial intermediaries, such as banks or other financial institutions.
Growing Institutional Interest: Over time, digital advertising gained significant institutional interest as advertisers and marketers recognized its potential for more targeted, cost-effective advertising, and more discernable return and payback metrics. Similarly, Bitcoin and DLT have attracted venture capital firms, technology companies, and other traditionally early investors that recognized the potential for decentralized finance, secure, immutable transaction processing, and other benefits of blockchain technology.
Initial Skepticism and Regulation: Both digital advertising and Bitcoin/DLT faced initial skepticism and regulatory challenges. Digital advertising faced scrutiny, and regulatory frameworks needed to adapt to new forms of online advertising to address consumer protection and privacy concerns. Similarly, bitcoin and cryptocurrencies encountered market skepticism and continue to face regulatory scrutiny as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and other financial regulators seek to better understand and regulate this new asset class.
Importantly, it’s in this regulatory oversight where we have just recently seen a potential framework developing for much-needed regulatory clarity. The SEC has long come under fire for its approach of regulating crypto markets by enforcement, rather than providing proactive, definitive regulatory guidance. After arguably being found asleep at the wheel in the aftermath of the FTX debacle, the SEC has become a more consistently active regulator. In a watershed event, the SEC sued Coinbase (NASDAQ: COIN) and Binance, two of the world’s largest crypto exchanges, in June 2023 for allegedly breaching SEC securities regulations. The SEC alleged Coinbase traded at least 13 crypto assets that the SEC deemed to be securities which should have been registered with the SEC. (Ironically, the SEC reviewed Coinbase’s initial public offering of securities in April 2021 and did not object to the Company’s public listing.) The SEC accused Binance of offering 12 cryptocurrencies without registering them as securities.
The SEC’s litigation claims center around whether crypto tokens represent investment contracts and/or securities. Given the technological innovations and new business models involved with crypto assets, this is a substantially gray area that will ultimately be decided by the courts. Just last week a judge ruled in a split decision in the SEC’s earlier lawsuit against Ripple that Ripple’s XRP token was a security sometimes.
Although there has been a long-running debate as to whether some cryptos are securities, there has been very little argument from the SEC that Bitcoin is a security. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) ruled in 2018 that “virtual currencies, such as bitcoin, have been determined to be commodities under the Commodity Exchange Act (CEA)” in its Bitcoin Basics brochure.
Despite this seeming clarity for bitcoin’s treatment as a commodity, the SEC has denied dozens of registrations for spot bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) of commodity-based trust shares over the last few years. Paradoxically, the SEC has allowed numerous ETFs based on bitcoin futures to trade on regulated exchanges but has denied every spot bitcoin application that has been submitted to date. The SEC has often cited that the underlying spot market of Bitcoin is subject to fraud and manipulation. Since the derivatives market reflects spot prices, it is difficult to see the SEC logic in allowing the futures-based ETFs but not ETFs based on the underlying bitcoin.
However, it seems that regulatory clarity is about to arrive for Bitcoin with the recent submission by Blackrock (NYSE: BLK) for a spot Bitcoin ETF. We see the SEC approval of a spot bitcoin ETF akin to the REIT structure that democratized cell tower and data center ownership to the masses. Blackrock is the world’s largest investment manager at $9 trillion in assets under management (AUM). It’s CEO, Larry Fink, was an early skeptic and once declared, “Bitcoin is nothing more than an index for money laundering.” Funny how profit incentives and client defections to your competitors providing Bitcoin access will change your tune.
On July 13, the SEC added BlackRock’s spot Bitcoin ETF application to its list of proposed rulemaking filings for the NASDAQ stock market. This move may signal the SEC’s intent to take the application more seriously after BlackRock added a “surveillance-sharing” agreement with U.S. crypto exchange Coinbase to its updated application. Blackrock’s competitors Fidelity Investments, WisdomTree, Invesco, VanEck, and others have followed suit and filed similar “surveillance-sharing” amendments to their respective bitcoin ETF applications. Several of these other bitcoin ETFs were recently added to the SEC’s review docket.
It is particularly interesting to note that both the NASDAQ exchange and CBOE are partnering with Coinbase to provide the market surveillance function to address SEC concerns about monitoring of fraud. The Coinbase name was originally omitted in Blackrock and other bitcoin ETF applications, possibly due to the SEC’s wide-ranging enforcement action against Coinbase.
In addition to the spot bitcoin ETFs, there have been several other positive institutional moves that may also promote bitcoinalization:
- Not to be left out, rumors abound that Vanguard ($7.6 trillion in AUM) may potentially take over the Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC) and convert it into a spot ETF.
- Last September, Fidelity Investments, Schwab and Citadel announced they were teaming up to launch a new crypto exchange called EDX.
- Fidelity Investments is no stranger to bitcoin. Fidelity has been leading the institutional adoption of bitcoin. For example, Fidelity has its own bitcoin mining operation. And since early last year, Fidelity has enabled their 73,000 retirement plan clients to make bitcoin allocations with 401K plans where Fidelity acts as the custodian or administrator.
- More recently Fidelity Investments began rolling out Fidelity Crypto® capabilities to its Fidelity Institutional Registered Investment Advisory (RIA) network and family office clients by providing access to Fidelity Digital Assets custody and execution services within the RIA Wealthscape platform.
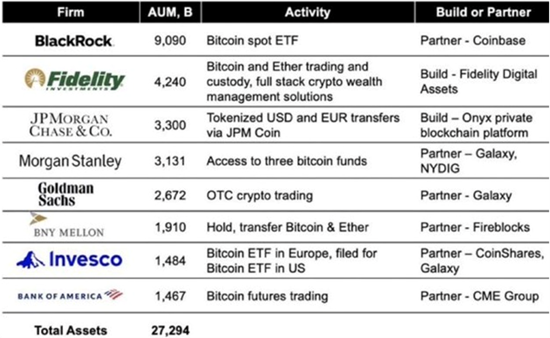
All the foregoing developments are elegantly summarized in the following chart from BitcoinNews.com. Led by Blackrock and Fidelity, the following institutions which control some $27 trillion in assets under management are queuing up to invest in a scarce 21 million bitcoin (19.4 million in existence and 1.6 million left to be mined).
Considering the foregoing, we will be taking the following actions on behalf of our Servant Financial clients:
- Doubling portfolio allocations to the bitcoin sector – initial client allocations based on account risk tolerances were to Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (OTC: GBTC) ranging from 1% to 2% and Hut8 Mining (NASDAQ: HUT) of 1.5% to 2.0%,. HUT’s stock price has doubled in the last 45 days on the bitcoin rally on news of Blackrock’s ETF filing and company specific merger developments. We’ve simply doubled the HUT allocation in more risk-tolerant client accounts that hold this security without making additional share purchases. Concerning the direct bitcoin allocation, we are withholding action on any additional GBTC allocations until we’ve had an opportunity to meet with Fidelity Investments on the Fidelity Crypto® integration for registered investment advisors. Initially, Fidelity will not be charging custodial fees for cold storage of client Bitcoin or Ethereum. Over time, Fidelity intends to charge 0.4% for Bitcoin and Ethereum custody. GBTC charges a 2% annual management fee.
- Continuing Professional Education – taking an online course for a certificate in blockchain and digital assets for financial advisors offered by Digital Asset Council for Financial Professionals.
- Ongoing securities research – analysis of other leading “picks and shovels” companies in the bitcoin and blockchain ecosystem like HUT. We are beta-testing a more speculative pure-play model invested in six companies for one client.
- Convergence of bitcoin miners and their high-performance computing capabilities with artificial intelligence applications – it’s a story for another day but a convergence of artificial intelligence and bitcoin mining/high-performance computing is anticipated. It seems that bitcoin mining equipment is uniquely suitable for artificial intelligence applications, particularly NVIDIA graphics processing units (GPUs, initially developed for gaming and graphics applications) with application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) for bitcoin mining. Some miners established early strategic relationships with NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA).
“I love this stuff – bitcoin, Ethereum, blockchain technology – and what the future holds.” – Abigail Johnson, granddaughter of the late Edward C. Johnson II, founder of Fidelity Investments.
And just like that bitcoin is institutional – bitcoinalization.