Reminiscent of the 1984 Bonnie Tyler hit from Footloose, many US employers are crooning for working class heroes. “I need a worker, I’m holding out for a worker ‘til the end of 2023.” The U.S. labor force has been dwindling from food and beverage service to financial analysts since the COVID-19 pandemic began. While some have been quick to blame the shortage on several rounds of government relief money that idled some workers, a combination of factors is influencing this labor change. Millions of people were suddenly unemployed at the start of the pandemic and many industries assumed these people would return to work when normalcy resumed. However, almost 3 years after the start of the pandemic, these “missing” workers may never return to the labor force. This labor shortage could cause a secular shift in American businesses and labor markets.
COVID-19
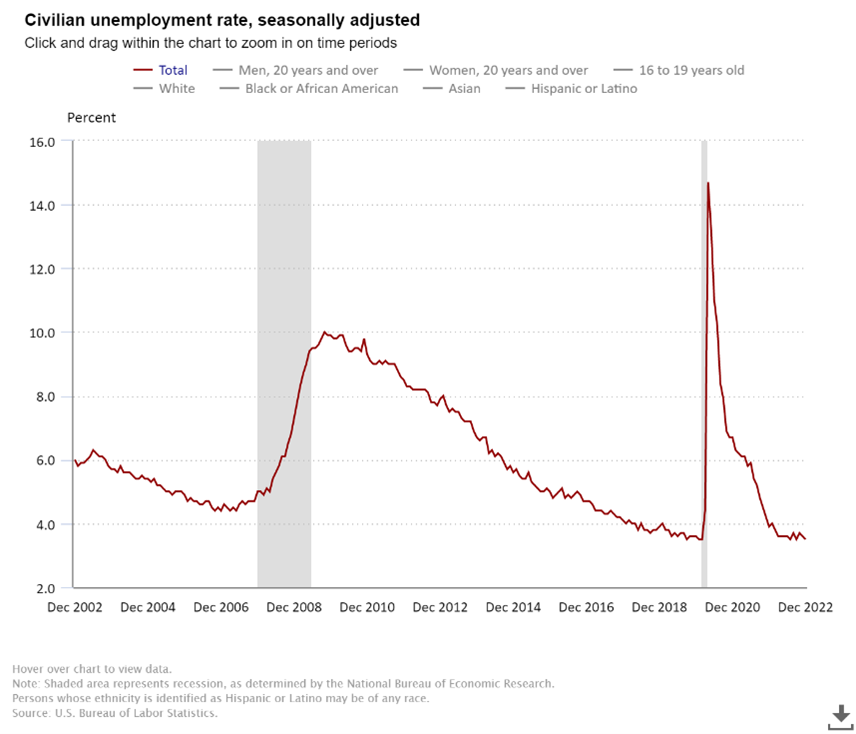
Government and businesses’ responses to COVID-19 brought about a 50-year high in unemployment, peaking at 14.7% in April 2020. Service workers and business professionals found themselves suddenly without work and wages. The U.S. government came to the rescue, handing out $5 trillion in pandemic stimulus money with a large portion devoted directly to individuals in the form of stimulus checks and extended unemployment benefits. When evidence of a growing labor shortage emerged, many people pointed fingers at the U.S. government for providing so much monetary support and disincentivizing workers to return to the job market. However, the story isn’t that simple. Fears of contracting and spreading COVID and the existential risk of mortality created a widespread shift in lifestyle priorities and an increased desire for a better work-life balance. The result of these factors has been the rise of remote labor and gig workforces. A study done by the U.S. Chamber of Commerce found 91% of survey participants hoped they could continue to work remotely at least part of the time. Businesses have generally adapted to this desire and been accommodative. However, remote labor isn’t really a possibility for customer-facing service roles or manufacturing jobs for which labor activities are concentrated in a single location.
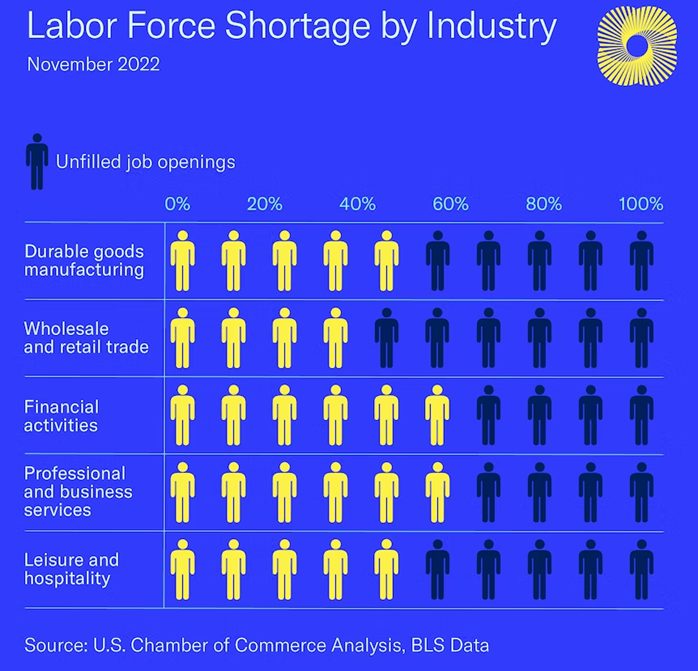
The U.S. Labor Department reported 10.5 million job openings in November 2022 with the labor participation rate at 62.3%, down from 63.3% in February 2020. Not only do service industries have their “Help Wanted” signs out but so do financial services and professional and business services. While workers are demanding more remote work, these professional industries are demanding people come back to work in their office buildings to collaborate with their colleagues. Workers have been less receptive to this return to the office mandate causing worker turnover rates to reach 57.3% in 2021, up from 45% just two years earlier. Businesses that have been able to accommodate their workforce’s desires for at least partial remote work are generally experiencing lower turnover and avoiding severe labor shortages.
No More Baby Boomers
Economists argue that this labor shortage was always on the demographic table. The labor participation rate has been on a downward trend since 2000 and some argue it is as simple as the laws of supply and demand. One of the largest generations in U.S. history, the Baby Boomer generation, is clocking out with no plans to punch back in. The median age of the Baby Boomer generation (born 1946-1964) turned 66 last year meaning many boomers are taking a refrain from Johnny Paycheck’s 1977 hit song, “Take This Job and Shove It” and checking into retirement. The next generation behind the boomers, Generation X, is about 5 million people short to fill the employment hole the boomers are leaving. The next generation able to take the Boomer’s place is the Millennials; however, it is still going to be several years before they enter the labor force. COVID-19 only intensified Boomers leaving the workforce as older generations were more susceptible to adverse outcomes from the virus. Boomers were also less likely to adapt to changes toward more remote work. This trend may have something to do with the adage of old dogs and new tricks.
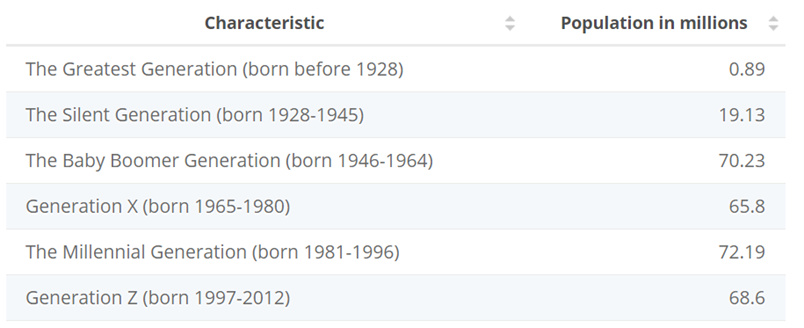
Source: Statista
These trends in labor demographics are not likely to be resolved any time soon as the World Bank projects the number of people between the working ages of 15 and 65 is set to decline by 3% over the next decade. “Without sustained immigration or a focus on attracting workers on the sidelines of the labor force, these countries simply won’t have enough workers to fill long-term demand for years to come,” said the chief economist at Indeed. Historically, immigration and globalization have helped bridge the labor gap; however, during the pandemic we saw a reversal of both trends. Policy reform towards immigration will need to happen if the U.S. wants a sufficiently dynamic labor force in the years to come.
Is the End in Sight?
The question begs, how long will this domestic labor shortage last? While a body of evidence suggests this is a systematic change, other economists argue a potential shift into a recession could help lower demand for labor and bring the labor situation towards equilibrium. The shifting landscape of the U.S. economy toward a recession would likely reduce hiring levels as companies are forced to cut back on growth plans. While we may see an uptick in unemployment levels, it is doubtful it will reach the near 10% unemployment levels the Great Recession of 2008 brought. The looming recession and persistent inflation point to a normalization of the labor market in 2023; however, some companies are still going to need to make adjustments to their business models to compensate for the loss in workers.
Companies are beginning to readjust their hiring strategies and their job expectations to accommodate the current labor market conditions. Inflation has made it difficult for companies to keep pay scales in line with the cost-of-living increases. It is going to be increasingly important for companies to be proactive with their employment strategies and stay ahead of the trends in worker lifestyle demands if they want to retain good talent. Companies such as IBM (Ticker: IBM) predicted this shortage long ago and began outsourcing their talent to countries with growing populations such as India. They have been able to capitalize on lower market-based wages in these developing countries and cheaper input supplies.
Meanwhile, the technology sector is busily working on solutions to these labor shortages, like artificial intelligence and machine learning. The most recent market hero in this space is ChatGPT from the venture firm OpenAI. ChatGPT optimizes language models for dialogue. The ChatGPT model has been trained to interact with users in a conversational way. This format makes it possible for ChatGPT to answer follow-up questions, admit its mistakes, challenge incorrect premises, and reject inappropriate requests. Several in the Twittersphere claim that ChatGPT has passed portions of the Bar Exam, medical license exam, and MBA operations exam. Further, experts interviewed by UK’s Daily Mail believe ‘AI will take 20% of all jobs within five YEARS’ and explain how bots like ChatGPT will dominate the labor market. According to the article, Microsoft invested $10 billion in ChatGPT and said that the technology will change how people interact with computers.
From our standpoint, the best way for investors to express a purposeful view on the future emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning is through the leading technology heros, like Microsoft and Apple, who have massive distribution capabilities through their existing software and hardware product suites and business relationships across sectors. We like iShares U.S. Technology ETF (IYW). This ETF provides exposure to the leading U.S. electronics, computer software and hardware, and IT companies. IYW’s boasts assets under management totalling $7.8 billion and a reasonable expense ratio of 0.39%. IYW has traded down 35% in 2022 and trades at an estimated 2023 price to earnings ratio of 23 times. The following summarizes IYW’s top holdings:
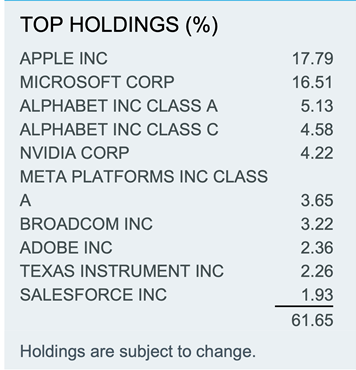
We recommend buying IYW on future weakness and sitting on the sidelines holding out for a hero ‘til the morning light. In other words, wait until the next recession and buy these tech heroes who are strong, fast, and fresh from the fight.